-
위치서울시 용산구 한남동
-
용도연립주택
-
대지면적767.00㎡
-
건축면적230.04㎡
-
연면적1274.32㎡
-
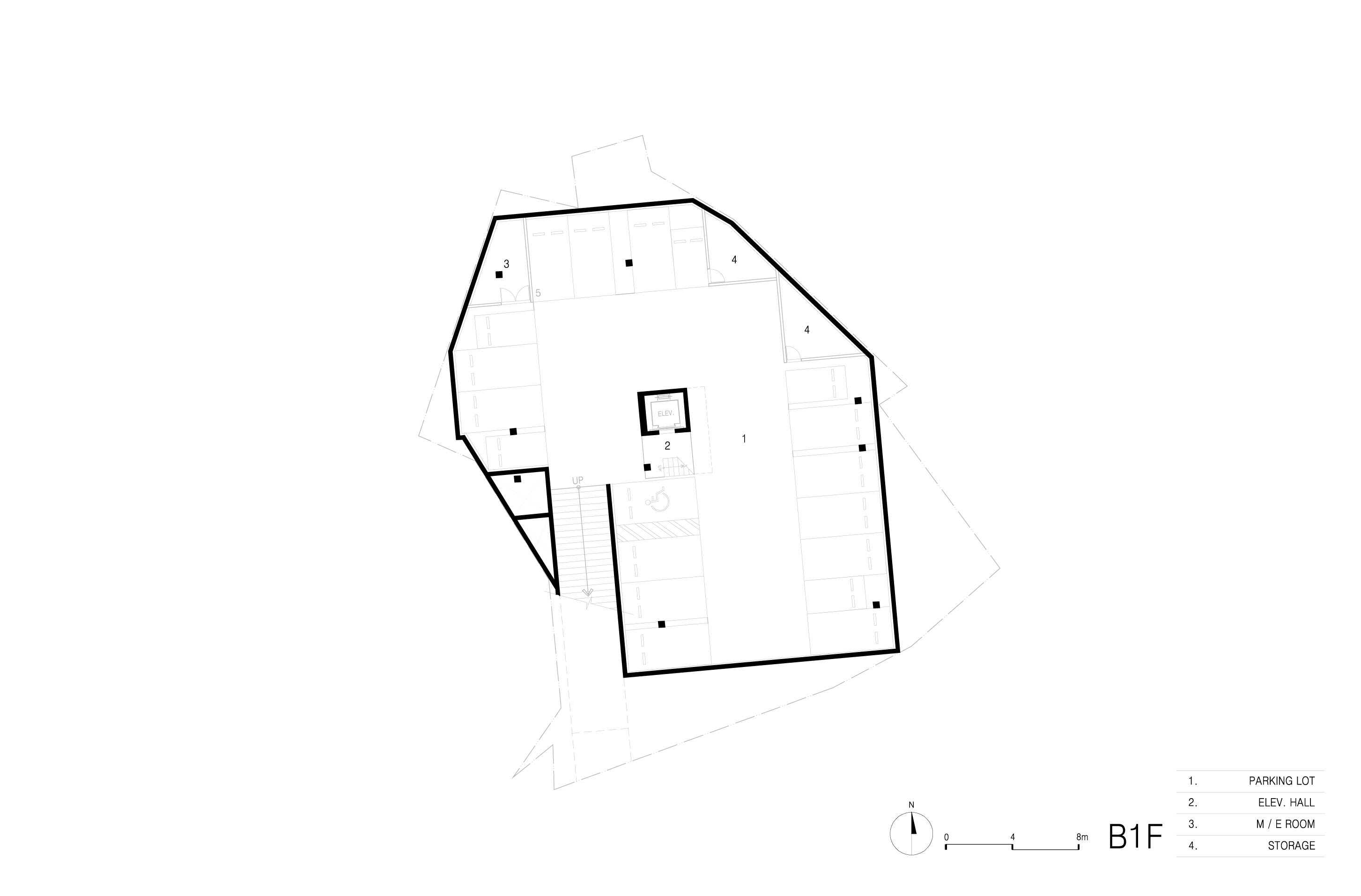
규모지하1층, 지상3층
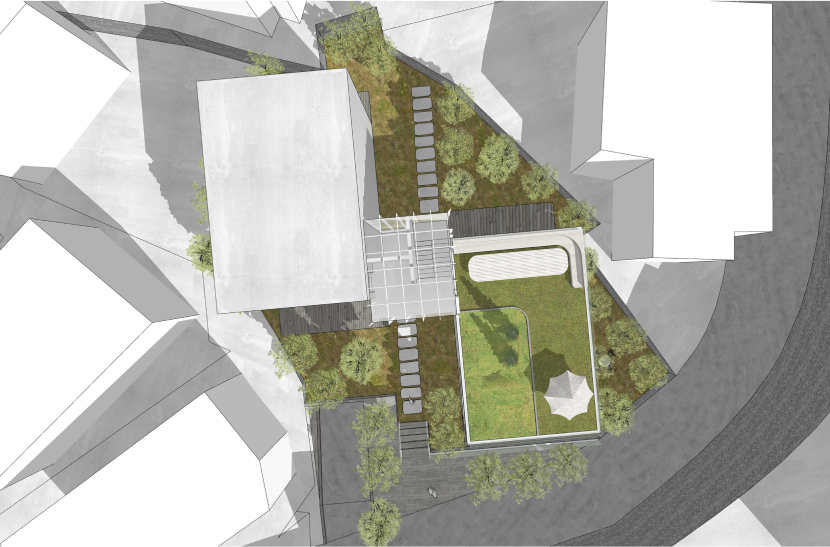
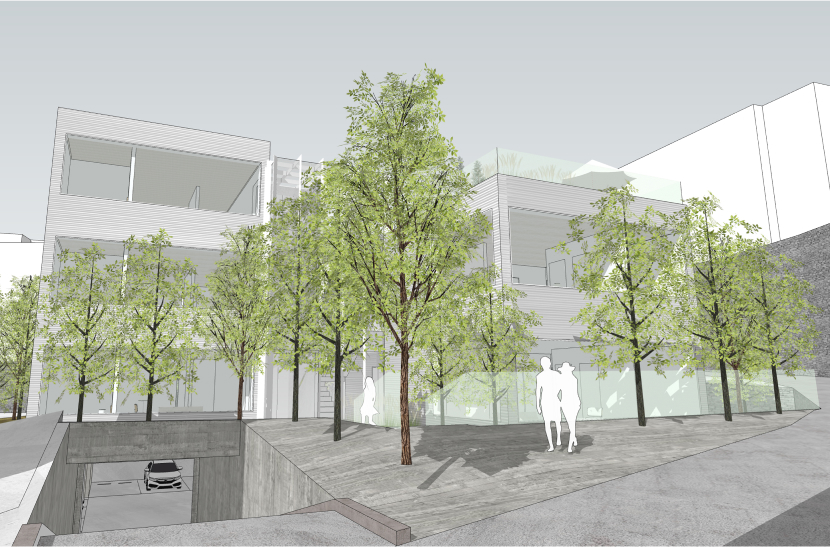
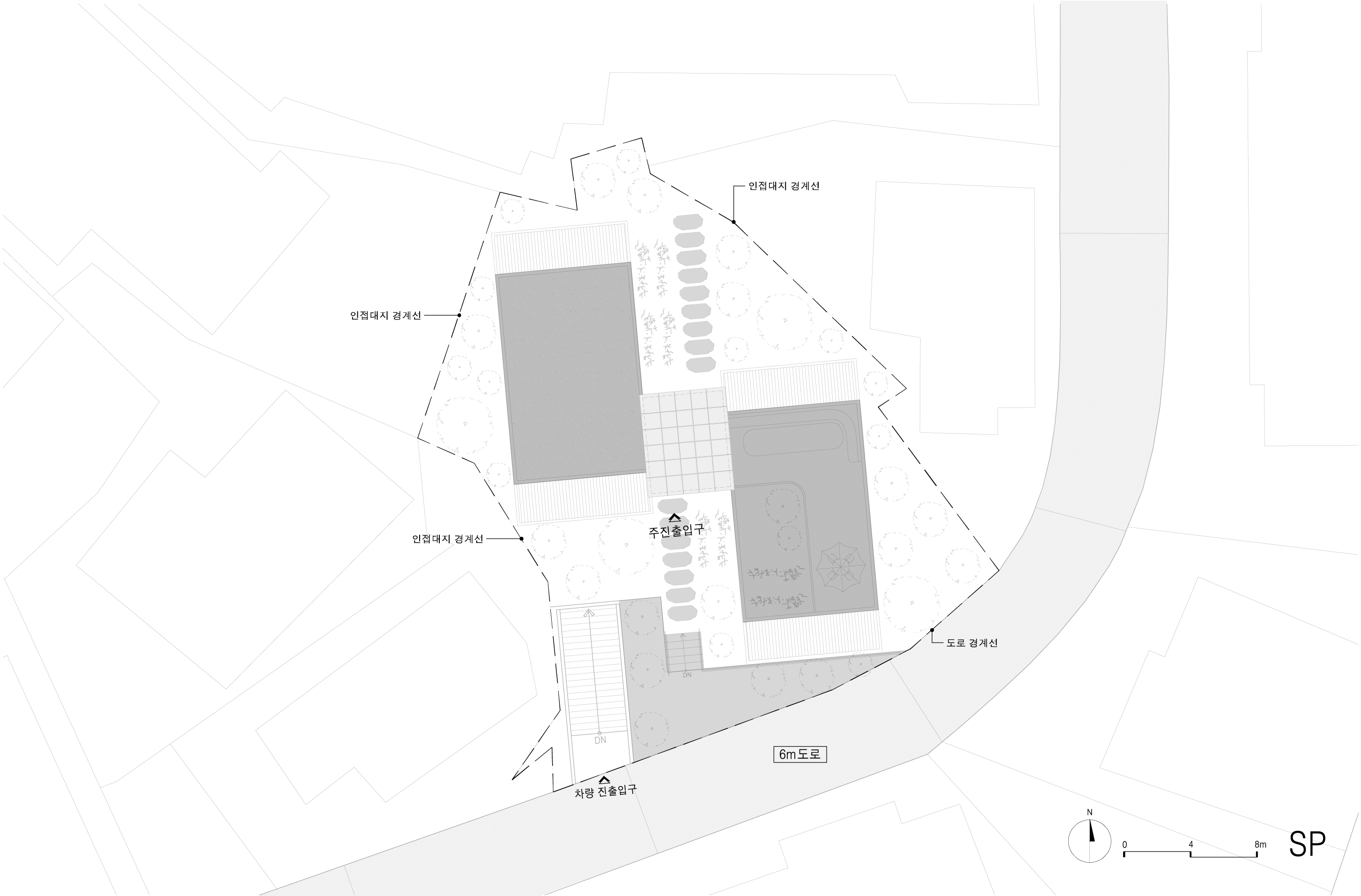
이 연립주택은 경사 지반에 주변 주택 밀집 속에서 대지의 형태가 이형으로 대지 현황이 형성되어 있다. 더불어 지구단위계획 상 자연경관지구에 속하게 되어서 보다 제한적인 건폐율을 적용 할 수 밖에 없게 되어 외부공간의 활용이 중요하게 되어졌다.
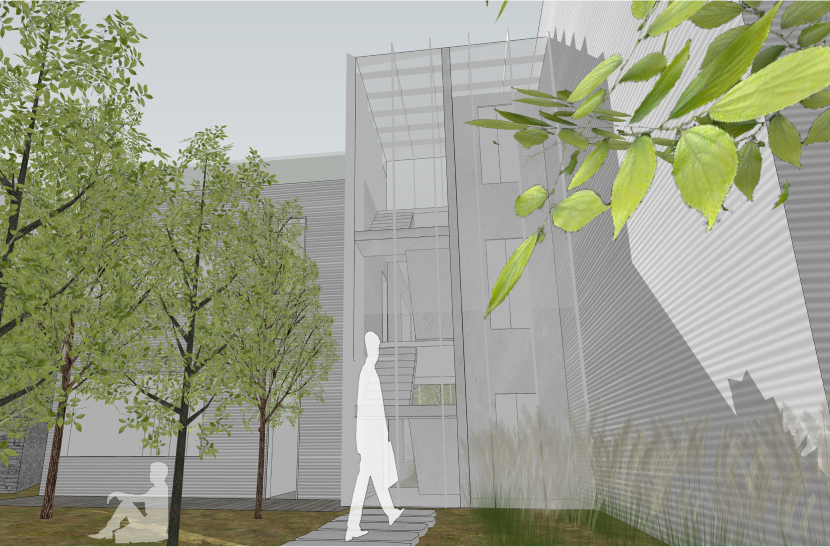
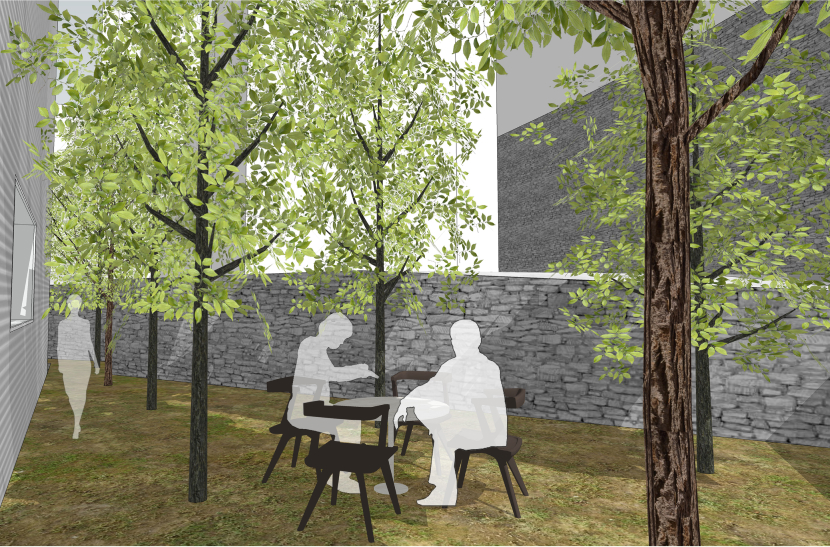
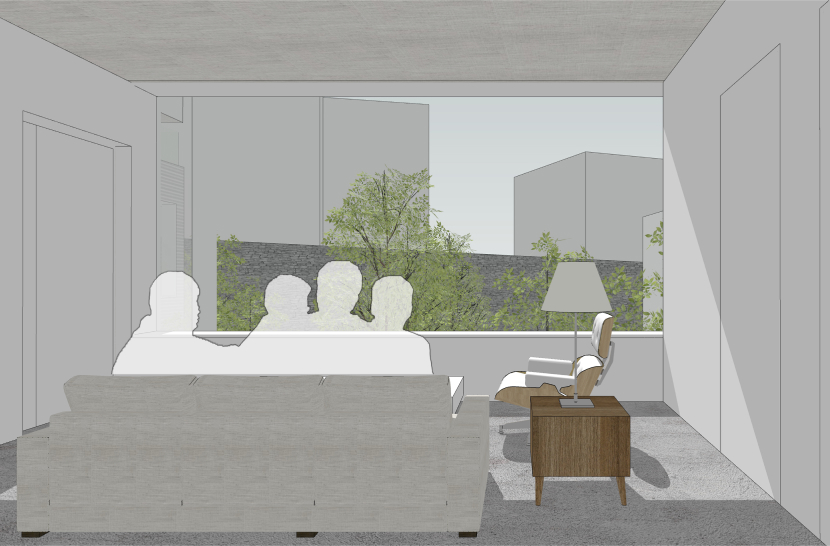
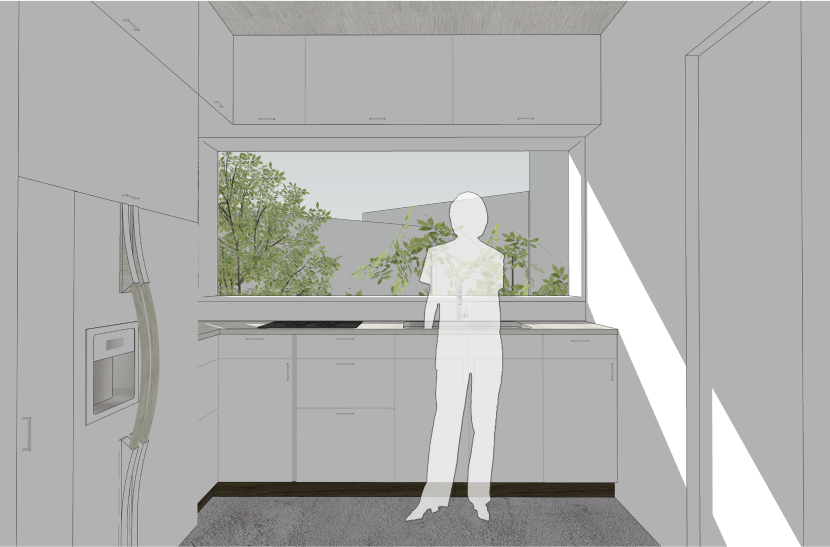
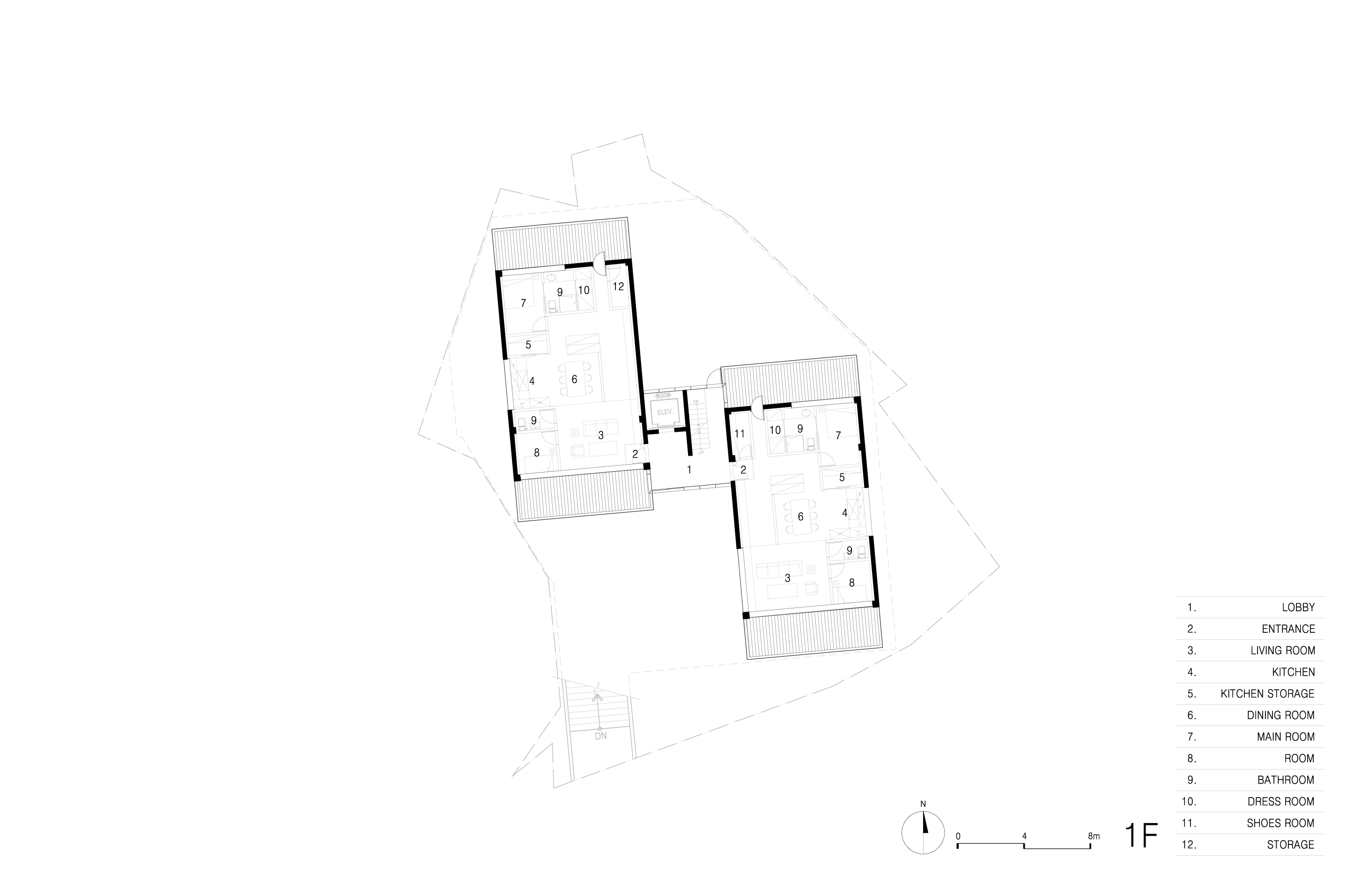
이에 따라 경사 및 이형의 대지를 활용 건물 면마다 외부공간이 면하게 하여 1층 거주민의 활용도를 높이고 2층 이상에서는 식재로 인한 자연현상을 볼 수 있도록 하였다.
In this row house, the land status is formed due to be close by the land in the concentration of surrounding houses on the inclined ground. In addition, as it belonged to the natural landscape district according to the district unit plan, it was forced to apply a more limited building-to-land ratio, and the use of external space became important.
Accordingly, the use of inclined and deformed land was made to face the external space on each side of the building, thereby increasing the utilization of residents on the first floor, and natural phenomena caused by planting can be seen on the second floor or higher.